datacenter
Analysis of the Current Coherent Optical Module Market
Researchers have made great progress in optical devices. The output power of laser, linewidth, stability and noise, as well as the bandwidth of photodetectors, power capacity and common mode rejection ratio have been greatly improved. Microwave electronic devices have also been greatly improved. Then, the coherent optical communication technology has gradually become an important capacity-lifting solution for the current 100G line-side.
Market Demand for Coherent Optical Communication
One of the biggest drivers of growth in the current communications market is the transition from 10G to 100G in the metro, core and Data Center Interconnect (DCI) sectors.
With the explosive growth of information generated by the use of communication technologies such as video conferencing and the spread of the Internet, the market has proposed higher transmission performance requirements for the physical layer that is the basis of the entire communication system.
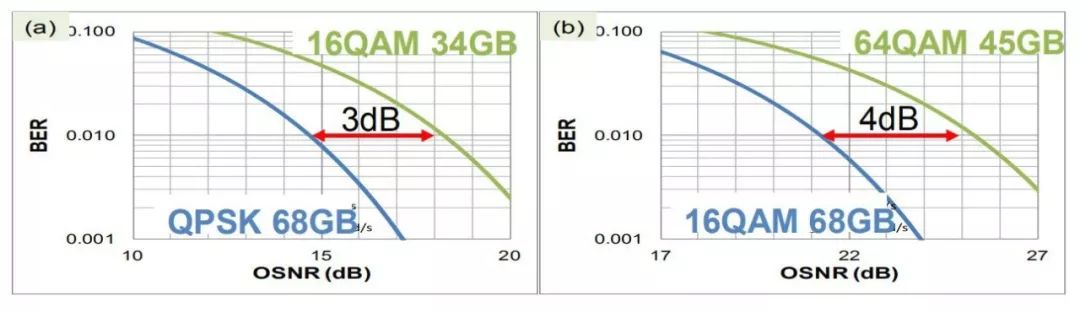
In terms of digital communication, how to expand the capacity of C-band amplifiers, overcome the deterioration of fiber dispersion effects, and increase the capacity and range of free-space transmission have become important considerations for researchers; in analog communication, sensitivity and dynamic range are key parameters of systems.
Driven by strong demand, large-scale DWDM systems are gradually depleting their wavelength resources, and the efficiency of Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) systems through compressed optical pulses also has a large technical bottleneck. People began to consider replacing the original Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) system with a coherent optical communication system.
Advantages of Coherent Optical Modules
The coherent optical communication system modulates the signal to the optical carrier by adjusting the amplitude, phase and frequency by means of external light modulation (such as DP-QPSK) at the transmitting end.
Compared with the traditional direct detection system, coherent detection can obtain more signal information through the signal light and the beat frequency of the local oscillator; after the signal reaches the receiving end, it uses high-speed Digital Signal Processing (DSP) technology to perform front-end processing such as equalization. The optical mixer and the optical signal generated by the local oscillator are coherently mixed to realize signal reconstruction and distortion compensation.

Coherent optics can be used in both 100G and 400G applications, primarily because it enables service providers to send more data over existing fiber, reducing the cost and complexity of network upgrades for bandwidth expansion.
- Coherent detection combined with DSP technology:
- Cleared barriers to traditional coherent reception
- Compensate for various transmission impairments in the electrical domain, simplifying transmission links
- Make high-order modulation formats and polarization states possible
- At the same time, the application of high-order modulation formats enables coherent optical communication to have higher single-wavelength channel spectrum utilization compared to traditional system systems.
Coherent receivers have no special requirements for fiber channel, so coherent optical communication can use already laid fiber lines. With the aid of digital signal processing algorithms, coherent receivers compensate for signal distortion caused by fiber dispersion, polarization mode dispersion, and carrier phase noise at a very small cost.- A coherent receiver is about 20 dB more sensitive than a normal receiver, so the distance that is not relayed in the transmission system becomes longer, which reduces the number of amplifications in the transmitted light path.
Based on the above reasons, coherent optical communication can reduce the cost of optical fiber erection for long-distance transmission, simplify optical path amplification and compensation design, and become the main application technology of current long-distance transmission network.
Application Scenarios of Coherent Optical Modules
At present, the coherent optical communication is mainly used on the line side of the backbone network and the metropolitan area network, and belongs to the technical research field of DWDM long-distance transmission. In the application scenarios of the metropolitan area network and the core network with distance more than 80km, the coherent optical communication features good performance of Optical Signal-to-Noise Ratio (OSNR), sensitivity, dispersion tolerance and so on.
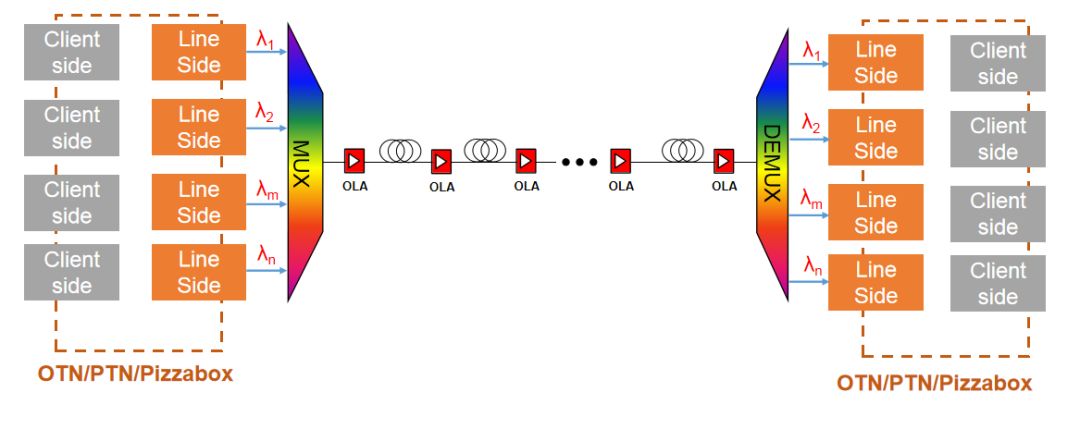
WDM System
The operating wavelength range is C-band (1530nm to 1565nm), and the fiber type is G.652D (prefered) or G.655. The key performance index is OSNR.
Error correction coding technology can jump out of the limitations of the physical layer of transmission, and compensate for all physical transmission impairments at the logic layer, especially the effects of nonlinear effects.

5G Middlehaul/Backhaul Network
In the 5G middlehaul scenario, 100G/200G DWDM system will be deployed, and the 100G CFP-DCO and 200G CFP2-DCO optical module can be used to implement the 80km scene application; the 400G DCO product is applied in the 5G backhaul scenario with distance less than 200km.
DCI
Whether the coherent communication will be used in the DCI field of 40km to 80km depends mainly depends on the commercial cost performance and whether the market capacity is large enough.
At the current 100G rate, products such as 100G ER with EML modulation are sufficient for the use; the 100G CFP-DCO ZR series will appear in the future.
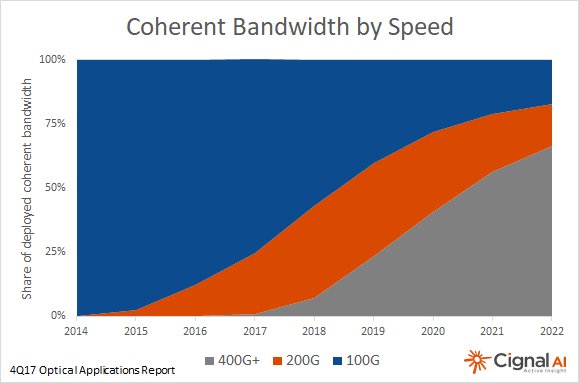
The OIF organization is developing a 400ZR specification that uses a combination of DWDM and coherent technology.
Andrew Schmitt, principal analyst at Cignal AI, said: "Coherent 400G will limit the development of existing 200G and 100G technologies by 2020, and new devices will maximize optical capacity without relying on coverage." Foreseeable Yes, more and more 400ZR products will enter the market.
Summary
The coherent optical communication system is a more advanced and complex optical transmission system suitable for longer distance and larger capacity information transmission.
At present, coherent modules with the CFP form-factor are bulky and consume large power. Compact coherent modules will replace existing coherent products. The innovation of semiconductor technology and the improvement of chip technology will greatly promote the replacement of 400G coherent products.
In recent years, Gigalight, a global optical interconnect innovator, has increased its research and development of coherent modules and has achieved a series of achievements. In the next few years, it will strengthen cooperation with the industry and jointly promote the progress of related industries.
Source: Analysis of the Current Coherent Optical Module Market
